COMPREHENSIVE AND EFFECTIVE
SCIENCE FORM 2
CHAPTER 4
HUMAN HEALTH
CONTENT
by Amelia Bashahruddin

by Amelia Bashahruddin
WATERBORNE
DISEASE
1. Waterborne diseases often occur during and after floods.
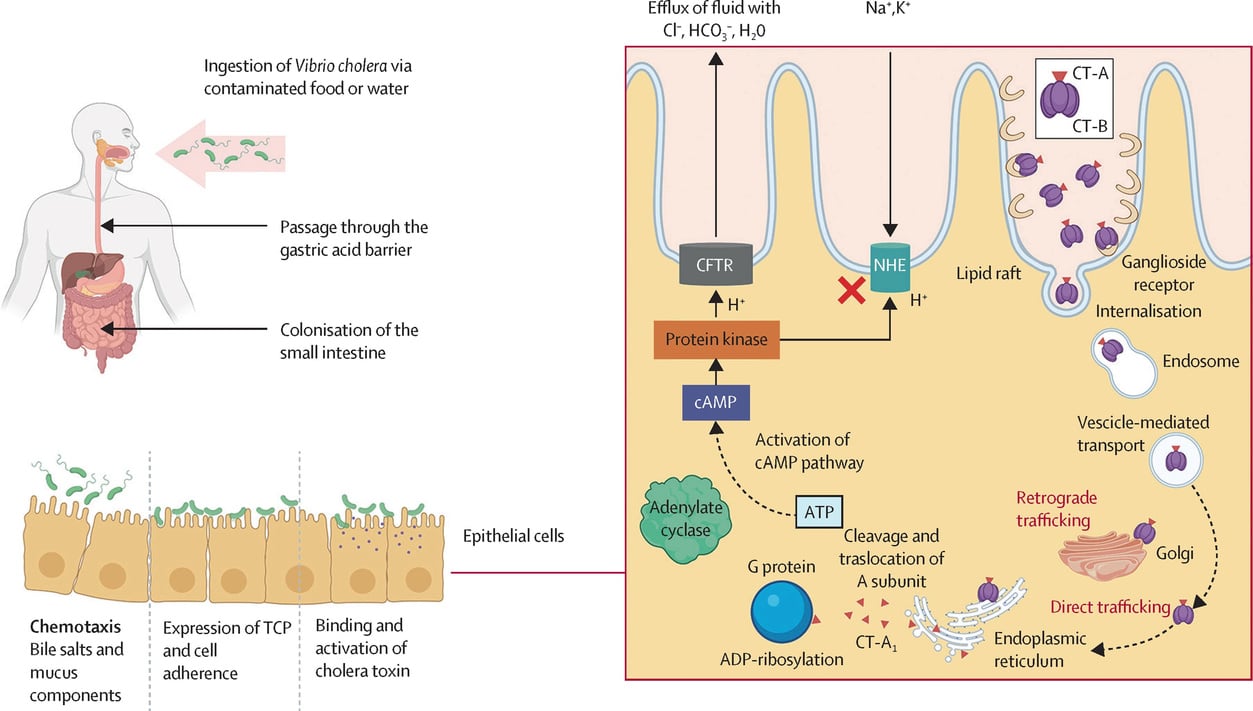
2. Cholera is an infectious disease transmitted through water.
3. Cholera is caused by the cholera bacterium,Vibrio cholerae.
4.Modes of transmission of cholera include
(a) food and drinks contaminated with cholera bacteria,
(b) sewage system, rubbish and faeces,
(c) patients who contracted cholera,
(d) houseflies which land on contaminated food and drinks.

Infection of Diseases through Contact

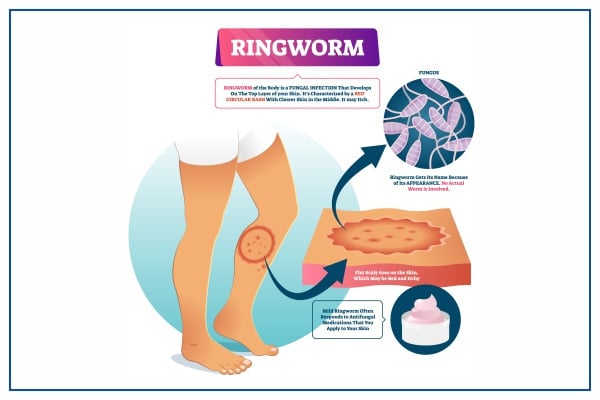
1. Infectious diseases spread through contact include ringworm and tinea.
2.Ringworm and tinea are caused by fungus or spores of fungus which normally get attached to personal belongings like combs and towels. When these personal belongings are shared, the fungus will infect the skin of the other user.
by Amelia Bashahruddin

Infection of Diseases through Vectors
by Amelia Bashahruddin
There are diseases transmitted by animals which transfer pathogens from one host to another new host. The animals are known as vectors. Examples of vectors are rats, mosquitoes, flies and cockroaches.
A. RATS
1. Infectious diseases spread by vectors like rats are leptospirosis (rat urine disease) that results from infection of the bacterium, Leptospira sp.
2. The Leptospira sp. bacteria is spread through rat urine which has been infected and remains infectious long as the urine is still moist.
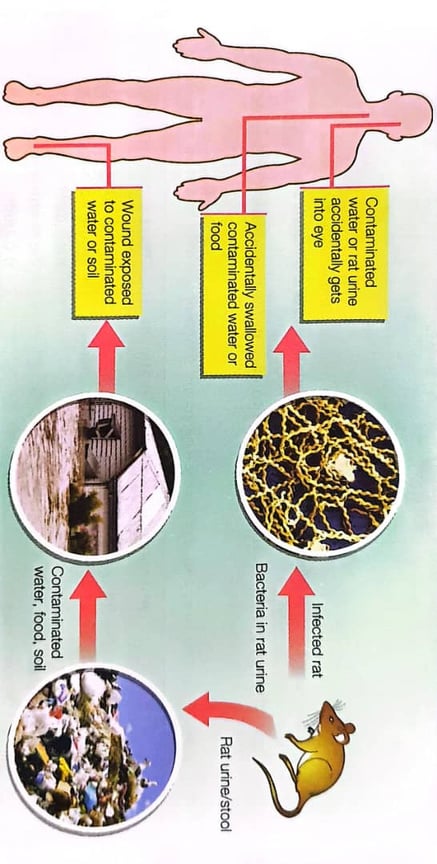
How rat urine disease or leptospirosis infects

B. MOSQUITO
1. Infectious diseases spread by vectors like mosquitoes are dengue fever, zika and malaria.
2. Pathogens like the dengue virus and zika virus are spread through bites by the Aedes mosquito while the parasite, plasmodium malariae (parasitic protozoa) is spread through bites from the Anopheles mosquito.
by Amelia Bashahruddin
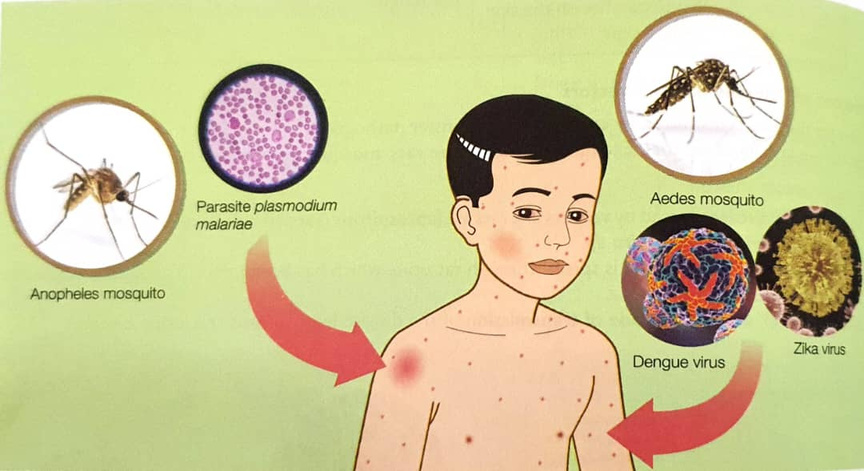
How infectious disease like dengue fever, zika and malaria are spread
4.2 BODY DEFENCE
The immune system is responsible for warding off diseases from harmful microorganisms. The three defence tiers comprise the skin and mucous membranes, phagocytosis, and the immune system.
First Line of Defence
A. Skin
1. Skin is made up of closely packed cells that form a physical barrier to prevent the entry of pathogens and protect the body.
2. Sebum and sweat are secreted on the surface of the skin to prevent the growth of microorganisms and destroy them.
3.Pathogens can only enter the body if there is an injury or a wound on the skin.
B. Mucus membrane
1.The mucus membrane is a layer that covers internal organs such as respiratory tract, digestive tract andexcretory system.
2.The mucus membrane secretes mucus to protect and trap microorganisms that enter the respiratory tract.3. There is fine hair or cilia on the respiratory tract to trap microorganisms and filter air.4. Lysosomes in tears act as an antiseptic enzyme to destroy bacteria.
by Amelia Bashahruddin
by Amelia Bashahruddin
Second Line of Defence
1. Second line of defence involves white blood cells to destroy microorganisms or pathogens that have successfully entered the body through the process of phagocytosis.
2. Phagocytosis is the process of engulfing, ingesting and digesting microorganisms or pathogens by whiteblood cells.
3. White blood cell will approach and surround a pathogen. Then, white blood cell will swallow and digest the pathogen.
4. Using phagocytosis, pathogens are destroyed and the body is prevented from contracting disease.
Third Line of Defence
1. Third line of defence depends on the body to resist certain diseasesby defending itself from certain pathogens.
2.This mechanism involves immune reactions.
3. These immune reactions produce special antibodies that areproduced by lymphocytes to protect the body from attacks bypathogens and antigens.
4. Antigens are foreign proteins found on the wall or outermembrane of pathogens. Antigens stimulate immune reactions.
5. Presence of antigens in the body stimulates white blood cells(lymphocytes) to produce special antibodies that act on the antigens.
IMMUNITY AND TYPES OF IMMUNITY
1. Immunity is the ability of the body to fight diseases that are caused by pathogens.
2. Immunity can be classified into two types, namely active immunity and passive immunity.
Active Immunity
1. Active immunity is obtained when the immunity system of an individual produces antibodies in response to immunity caused by a type of pathogen. Active immunity can normally last a long time up to several years or even a lifetime.
2. For example, a person who contracts chicken pox and then recovers will obtain active immunity from chicken pox for the rest of the person's life.
by Amelia Bashahruddin
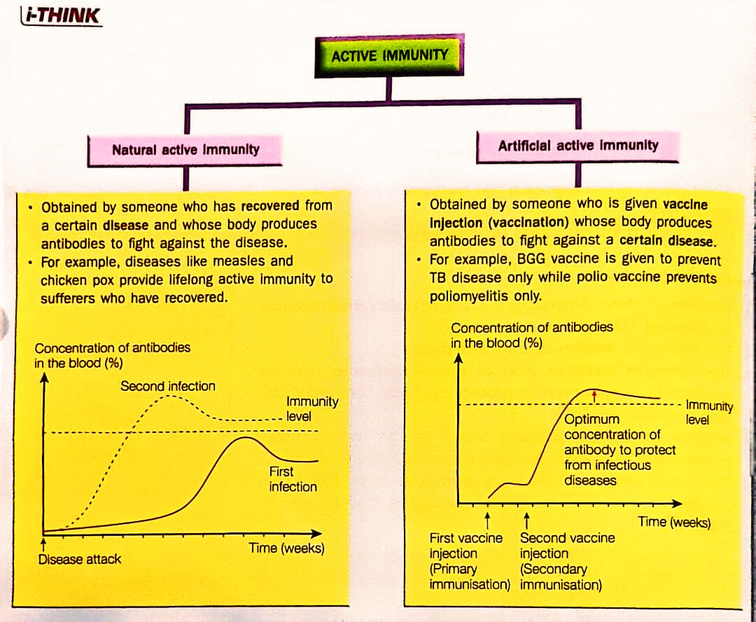
The types of active immunity.